Introduction: Beyond Simple Chatbots – The Rise of the AI Agent
The Buzz is Real: What’s All the Fuss About?
You’ve heard the term “AI Agent” buzzing around tech circles, news headlines, and maybe even your company meetings. It sounds futuristic, maybe even a little sci-fi.
But what are they, really? And why is everyone suddenly talking about them like they’re the next big leap? Forget the clunky chatbots of yesteryear that got stuck answering “What’s the weather?” AI agents represent a fundamental shift: moving from simple task automation to creating digital entities capable of autonomous, goal-oriented action. Think less “command-and-response,” more “here’s your objective, figure it out and get it done.”
Setting the Stage: From Automation to Autonomy
We’ve been automating tasks for decades. Think spreadsheets, basic macros, even early robotic process automation (RPA). These were powerful, but rigid. They followed strict rules. If something unexpected happened, they froze.
AI agents are different. They leverage the incredible reasoning and language understanding power of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Claude, or Gemini, but go a crucial step further.
They don’t just understand or generate text; they perceive their environment (digital or even physical), reason about it, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals, often learning and adapting as they go. It’s like upgrading from a pre-programmed toy car to a self-driving vehicle with its own sense of purpose.
Also Read – How to Build a Language Learning App Like Duolingo?
Demystifying the AI Agent: What Exactly Are They?
Core Definition: More Than Just Code
So, let’s cut through the hype. At its heart, an AI agent is a software solutions designed to perceive its environment, reason about it, make decisions, and take actions autonomously to achieve specific goals. It’s an autonomous entity operating within a defined sphere.
Imagine a highly skilled, tireless digital employee who can handle complex workflows involving multiple steps, tools, and decisions, all without constant hand-holding.
The Building Blocks: Key Components of an AI Agent
Think of an AI agent like a sophisticated robot, but primarily living in the digital world (for now!). Its “body” is made up of interconnected software components:
Perception: Sensing the (Digital) World
This is how the agent gathers information. It could be reading emails, analyzing sensor data, scraping websites, listening to customer calls (transcribed), parsing documents, or monitoring system logs. It’s the agent’s eyes, ears, and fingertips in its digital environment. Without accurate perception, the agent is flying blind.
Processing & Reasoning: The “Brain” (Often Powered by LLMs)
This is the core intelligence. The agent takes the perceived information and uses it to understand the current situation. This is where LLMs shine. They allow the agent to comprehend complex language, context, and nuance, reason through problems, infer meaning, and evaluate options. It’s not just pattern matching; it’s about understanding intent and implications. “Based on this customer’s angry email and their purchase history, what’s the real problem, and what’s the best path to resolve it?”
Decision Making: Choosing the Right Path
Based on its reasoning, the agent needs to decide what to do next to move towards its goal. Should it retrieve the customer’s order history? Escalate the issue? Offer a specific discount? Generate a personalized apology? This involves weighing options, predicting outcomes, and adhering to predefined rules or ethical guidelines. It’s about strategic action selection.
Action: Getting Things Done:
Decision made? Time to act! The agent interacts with the world to execute its plan. This could involve sending an email, updating a CRM record, placing an order in a system, generating a report, triggering another process, controlling a robotic arm, or even having a natural language conversation with a human. This is where the rubber meets the road – the agent produces tangible results.
Memory & Learning: Getting Smarter Over Time
Truly powerful agents aren’t static. They remember past interactions, decisions, and outcomes. This memory allows them to learn and improve over time. Did a particular approach resolve a customer issue quickly? The agent notes that for similar future cases.
Did an action cause an unexpected error? It learns to avoid that path. This feedback loop is crucial for long-term effectiveness and adaptability.
How Did We Get Here? The Evolution Towards Autonomous Agents
From Rules to Reasoning: A Brief History Lesson
The journey to AI agents has been long. Early “expert systems” in the 70s/80s tried to encode human knowledge as rigid rules. They were brittle and failed outside narrow domains. Then came machine learning, focusing on pattern recognition from data – great for predictions, but not for complex action.
RPA emerged to automate repetitive, rule-based digital tasks, a significant step, but still lacking understanding and flexibility. The missing piece was the ability to understand and reason in a human-like way within complex, unstructured environments.
Also Read – How to Patent a Mobile App: Step-by-Step Legal Guide
The LLM Catalyst: Fueling the Agent Revolution
Enter Large Language Models. The breakthrough capabilities of LLMs in understanding and generating human language, grasping context, and demonstrating emergent reasoning skills provided the crucial missing “brain” component. Suddenly, software could interpret complex instructions, understand the nuances of a user request or a system alert, and reason about the best next step in a way that wasn’t just pre-programmed.
LLMs became the powerful cognitive engines allowing agents to move beyond rigid rules towards true autonomy within defined scopes. It’s the combination of LLM smarts with the ability to perceive, decide, and act that defines the modern AI agent.
Why AI Agents Matter: The Game-Changing Potential
Okay, so they’re complex software entities. Why should you care? Why are businesses pouring billions into this space? Because AI agents offer transformative potential:
Hyper-Efficiency: Automating the Complex Stuff
Forget just automating data entry. Agents can handle entire multi-step processes that previously required human judgment and intervention. Think end-to-end customer onboarding involving document checks, system setups, and personalized communication – potentially managed autonomously by an agent. This frees up human talent for truly strategic, creative, or empathetic tasks only humans excel at.
24/7 Productivity: Your Digital Workforce Never Sleeps
Agents don’t need coffee breaks, sleep, or vacations. They can operate around the clock, handling customer inquiries across time zones, monitoring critical systems overnight, or processing orders while your human team rests. This leads to faster response times, continuous operations, and significant productivity gains.
Handling Complexity: Tackling Tasks Beyond Simple Scripts
The real magic lies in handling ambiguity and complexity. An agent can analyze a customer’s complaint, understand the underlying frustration (even if poorly expressed), cross-reference it with their account history, check policies, decide on a resolution path (e.g., refund, replacement, escalation), and execute the necessary steps – all autonomously. This level of nuanced task handling was previously impossible for traditional automation.
Personalization at Scale: Tailoring Experiences Dynamically
Imagine marketing campaigns that dynamically adjust for each individual based on real-time interactions, or customer support that feels deeply personal because the agent instantly recalls your entire history and preferences. AI agents can synthesize vast amounts of individual data to deliver hyper-relevant experiences to thousands or millions simultaneously, something humans simply cannot do manually at scale.
Unlocking New Possibilities: Innovation We Haven’t Even Imagined Yet
Agents are enabling entirely new applications. Imagine scientific research agents autonomously designing and running simulations, analyzing results, and proposing new hypotheses. Or personalized learning agents adapting curriculum in real-time based on a student’s progress and engagement. We’re just scratching the surface of what autonomous, intelligent software can achieve.
AI Agents vs. Traditional Bots & Assistants: Spotting the Difference
It’s easy to get confused. Let’s clarify the landscape:
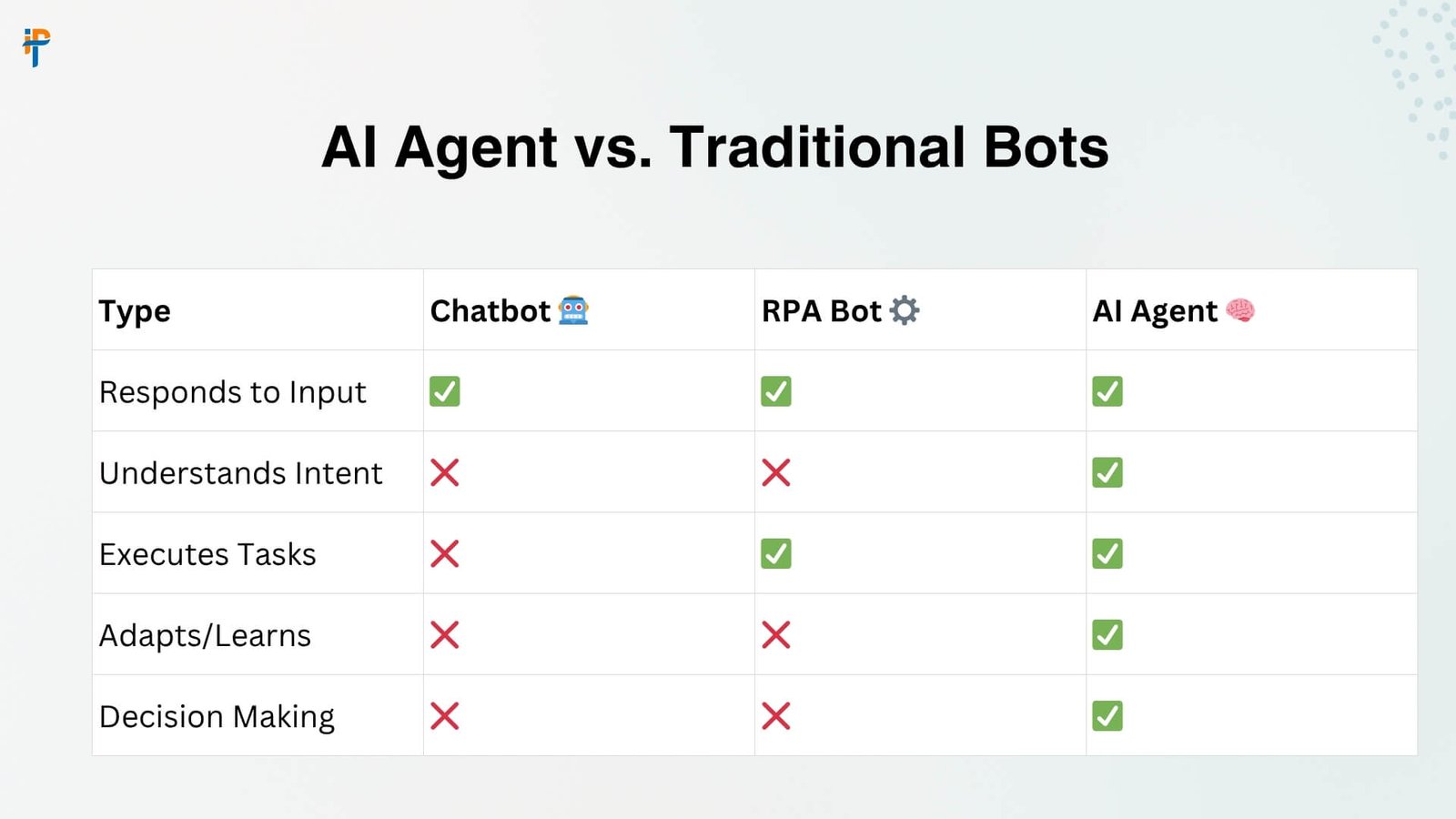
Chatbots: Answering Questions (Mostly)
Your classic website helper. Primarily reactive. You ask a question (“Where’s my order?”), it (hopefully) retrieves the answer from a knowledge base or simple database lookup. Limited reasoning, no complex action beyond fetching info. Easily stumped by complex or unexpected queries. Think: FAQ on steroids.
RPA Bots: The Rule-Following Clerks
Excellent at automating repetitive, high-volume, rule-based digital tasks. “If invoice arrives in email as PDF, extract data fields X, Y, Z, enter into system A, then send a confirmation email.” Very efficient within strict rules, but zero understanding or adaptability. If the invoice format changes, it breaks. Think: a very fast, very accurate, but very literal office clerk.
AI Agents: The Autonomous Problem-Solvers
This is the evolution. Agents understand context and intent. They reason about the best course of action. They decide and execute complex sequences involving multiple tools and decisions. They learn and adapt. They handle ambiguity. You give them a goal (“Resolve this customer’s complaint satisfactorily”), and they figure out the how, navigating the necessary steps autonomously. They combine the cognitive power of LLMs with the ability to act. Think: a proactive, intelligent, digital colleague.
Real-World Use Cases: Where AI Agents Are Making Waves TODAY
Enough theory! Let’s see where these digital powerhouses are actually flexing their muscles right now:
Revolutionizing Customer Service
Beyond FAQ Bots: Complex Issue Resolution: Agents can handle intricate problems. A customer emails about a defective product and an incorrect charge. The agent comprehends both issues, retrieves order and payment history, checks warranty status, initiates a return label and processes a partial refund, all while maintaining a natural, empathetic conversation flow via email or chat – all autonomously.
Proactive Support & Personalized Engagement: Agents monitor customer behavior (e.g., struggling with a feature in an app) and proactively offer help via in-app chat. They can also analyze sentiment in support tickets to prioritize urgent cases or automatically trigger personalized follow-up messages after a purchase or service interaction.
Supercharging Sales & Marketing
Intelligent Lead Nurturing & Qualification: Agents don’t just send bulk emails. They analyze a lead’s website behavior, downloaded content, and email responses to understand their interests and stage in the buying journey. They then engage in personalized, multi-touch email or chat conversations, answering questions, providing relevant info, and dynamically qualifying the lead before seamlessly handing it off to a human sales rep when ready.
Hyper-Personalized Campaign Execution: Imagine an agent that dynamically generates unique ad copy, social posts, or email content tailored to micro-segments or even individuals based on real-time data, predicts optimal send times, and adjusts budgets across platforms autonomously to maximize ROI.
Transforming Software Development & IT Ops
Autonomous Debugging & Code Assistance: Agents can analyze error logs, trace code execution, identify potential bugs, suggest fixes, and even generate unit tests. They act as super-powered pair programmers, understanding developer intent and context to streamline coding.
Self-Healing IT Systems & Proactive Monitoring: Agents constantly monitor network health, application performance, and security logs. They can detect anomalies, diagnose root causes (e.g., “Server X is overloaded due to spike from Service Y”), and automatically execute remediation scripts (restart services, scale resources, block suspicious IPs) before humans are even alerted, minimizing downtime.
Optimizing Business Operations & Workflow
Intelligent Data Analysis & Reporting: Move beyond static dashboards. Agents can be tasked with: “Analyze last quarter’s sales data across regions and product lines, identify the top 3 underperforming areas, hypothesize causes based on market news and internal data, and generate a summary report with recommendations.” They fetch, clean, analyze, interpret, and report autonomously.
Automated Procurement & Supply Chain Management: Agents monitor inventory levels in real-time, predict shortages based on sales trends and lead times, identify optimal suppliers, negotiate prices within set parameters, generate purchase orders, and track shipments – automating a complex, multi-step process end-to-end.
Innovating Healthcare & Research
Personalized Patient Monitoring & Support: Agents can analyze data from wearable devices and patient-reported symptoms, flag potential health concerns to clinicians based on learned patterns, and provide patients with personalized medication reminders, lifestyle tips, or answers to common non-emergency questions.
Accelerating Drug Discovery & Scientific Research: Agents can autonomously search and synthesize vast scientific literature, design computational experiments, run simulations, analyze complex genomic or chemical data, identify promising drug candidates or research pathways, and generate hypotheses – drastically speeding up the research lifecycle.
Empowering Personal Productivity
The Ultimate Executive Assistant (Digital): Imagine an agent that manages your calendar intelligently (scheduling meetings considering priorities, travel time, preferences), filters and prioritizes emails, drafts responses, books travel based on your habits, researches topics for your next presentation, and summarizes lengthy documents – all proactively.
Personalized Learning & Skill Development: Agents can assess your current knowledge, recommend tailored learning resources (articles, videos, courses), create personalized study plans, quiz you adaptively, and provide explanations – acting as a dedicated, always-available tutor.
Also Read – How Much Does It Cost to Hire an App Developer in Dubai 2025
Human-Agent Collaboration: The Winning Formula
Agents aren’t replacing humans; they’re augmenting them. Design workflows where agents handle the routine, complex, or data-heavy lifting, and humans step in for high-level strategy, creative tasks, nuanced judgment, empathy, and overseeing the agents themselves. Define clear hand-off points.
Ethics, Safety & Governance: Building Responsibly
Bias: Agents trained on biased data will exhibit biased behavior. Actively mitigate this.
Transparency: Can you understand why an agent made a decision? (“Explainability” is crucial).
Safety & Control: Implement guardrails! Prevent agents from taking harmful actions or accessing unauthorized data. Ensure there’s always an “off switch” and clear human oversight mechanisms.
Privacy: Strictly adhere to data privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.).
The Future of AI Agents: Where Are We Heading?
This is just the opening chapter. The trajectory points towards:
Increased Sophistication & Capability
Agents will become more reliable, handle even greater complexity, reason with deeper understanding, and exhibit more robust “common sense.” Expect smoother interactions and more ambitious tasks being delegated.
Seamless Multi-Agent Collaboration (Agent Swarms)
Imagine teams of specialized agents working together. A customer service agent might collaborate with a billing agent and a logistics agent to resolve a complex issue holistically, communicating and coordinating autonomously. This “swarm” intelligence will tackle incredibly complex challenges.
Deeper Integration into Physical Worlds (Robotics)
The line between digital and physical agents will blur. AI agents will increasingly be the “brains” controlling robots in warehouses, factories, hospitals, and even homes, enabling true physical world autonomy.
The Path Towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
While true AGI (human-level or beyond intelligence across all domains) remains a distant and debated goal, the development of increasingly capable and autonomous agents is a significant step along that path. Each advancement in agent capability pushes the boundaries of what machines can achieve independently.
Conclusion: Embracing the Agent-Powered Future
AI agents represent a paradigm shift in how we interact with technology and automate our world. They’re not just faster bots; they’re intelligent, autonomous entities capable of understanding, reasoning, deciding, and acting on complex goals. From transforming customer experiences and supercharging productivity to accelerating scientific discovery and managing our daily lives, their potential impact is staggering.
The rise of AI agents is inevitable. The question isn’t if they will reshape industries and workflows, but how quickly and how effectively we can harness their power. By understanding what they are, why they matter, and where they excel today, businesses and individuals can start strategically exploring and implementing these powerful tools. Start identifying opportunities, prepare your data, prioritize ethical development, and foster human-agent collaboration. The future belongs to those who learn to work alongside these intelligent digital partners. The age of the AI agent is here – are you ready to embrace it?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an AI agent, and how is it different from a chatbot?
How are AI agents different from RPA bots?
What are the core components of an AI agent?
AI agents typically include:
- Perception: Gathering data from emails, logs, sensors, etc.
- Reasoning (LLM-powered): Understanding and interpreting data.
- Decision Making: Choosing the best action based on context.
- Action Execution: Carrying out tasks autonomously.
- Memory & Learning: Adapting from past experiences.
Why are AI agents becoming so popular now?
What are some real-world use cases of AI agents today?
- Customer Support: Handling complex queries, proactively assisting users.
- Sales & Marketing: Lead nurturing, hyper-personalized campaigns.
- IT & Development: Debugging code, monitoring systems, and auto-remediation.
- Operations: Data analysis, reporting, and procurement automation.
- Healthcare & Research: Patient monitoring, drug discovery.
- Personal Productivity: Acting as executive assistants or learning coaches.













.png)


